Introduction
In today’s electrical infrastructure, durability and efficiency are key. But how do we manage cables in harsh environments? The answer lies in FRP cable trays. FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) cable trays offer a reliable solution to support and organize electrical cables. Known for their lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties, FRP trays are increasingly popular in industries facing challenging conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits and applications of FRP cable trays. You’ll learn why they’re the go-to solution for modern cable management systems.

Understanding FRP Cable Trays
What Is FRP?
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fiberglass. This combination provides FRP with a strong, durable structure while keeping it light. Known for its resistance to corrosion, FRP is ideal for environments that would typically degrade metal materials. These characteristics make it a go-to solution for cable trays used in industries ranging from manufacturing to energy.
How FRP is Used in Cable Trays
FRP is incorporated into cable trays as a lightweight, corrosion-resistant alternative to steel or aluminum. These trays are designed to hold electrical cables safely while protecting them from environmental damage. The trays’ robust construction ensures that cables are securely supported, which is essential in preventing damage that can disrupt operations. FRP cable trays can be customized for specific installations, with different tray designs that offer flexibility for diverse industrial needs.
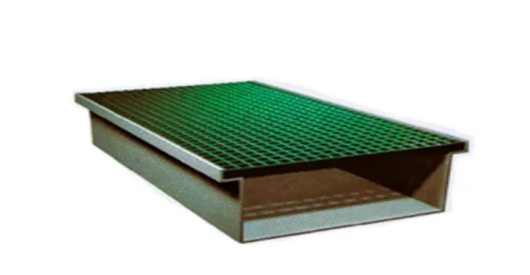
Different Types of FRP Cable Trays
There are three primary types of FRP cable trays:
● Ladder Type Cable Trays: These are the most common and are ideal for heavy-duty installations where multiple cables need to be secured and supported.
● Perforated Type Cable Trays: Best for lighter applications where airflow around cables is necessary, these trays come with holes to allow air circulation.
● Solid Bottom Cable Trays: These are suitable for situations where the cables need more protection from the elements or from physical damage.
Here’s a quick comparison of the different types of FRP cable trays:
Tray Type | Best For | Features |
Ladder Type | Heavy-duty, large cable installations | Provides maximum support and secure cable management |
Perforated Type | Lighter applications with cable airflow needs | Allows for better ventilation and less weight |
Solid Bottom Type | Applications requiring extra protection | Offers a higher degree of protection against physical damage and dust |
Advantages of FRP Cable Trays Over Traditional Materials
Corrosion Resistance
One of the standout features of FRP cable trays is their ability to resist corrosion. In environments exposed to water, chemicals, or even salty air, FRP cable trays do not rust or degrade like their metal counterparts. This corrosion resistance makes them ideal for industries such as chemical processing, marine, and wastewater management, where traditional materials might fail.
Lightweight Yet Durable
FRP cable trays are lighter than metal trays but equally strong. This unique combination of lightweight design and durability makes FRP easier to handle and install. The reduced weight also contributes to cost savings in shipping and installation, making FRP a more affordable option for large-scale projects. Despite their light weight, FRP trays provide the necessary structural integrity to support heavy cable loads.
Low Maintenance Costs
FRP cable trays require less maintenance than traditional materials like steel or aluminum. The lack of rust and corrosion means fewer repairs, and the durable nature of the material ensures that the trays continue to perform for many years. This translates to significant long-term savings on maintenance costs, making FRP an investment that pays off over time.
Applications of FRP Cable Trays
Industrial and Commercial Use
In industrial settings, FRP cable trays are crucial for managing cables in environments where heavy machinery and equipment are in constant operation. Chemical plants, manufacturing facilities, and marine applications benefit from the durability and corrosion resistance of FRP trays. These trays help maintain organized cable systems that can withstand the wear and tear of high-energy environments.
Energy and Utility Sector
FRP cable trays play an essential role in the energy sector. Power plants, oil rigs, and solar farms rely on FRP trays to manage their electrical infrastructure. The trays provide a secure pathway for cables, ensuring that energy is distributed efficiently and safely. FRP’s resistance to chemicals and harsh weather makes it an ideal choice for outdoor installations in utility sectors.
Public Infrastructure
FRP cable trays are also widely used in public infrastructure, such as airports, hospitals, and commercial buildings. These environments require robust cable management systems that meet safety and efficiency standards. FRP trays are particularly valuable in these settings due to their fire resistance, lightweight properties, and ability to withstand corrosive conditions.
FRP Cable Tray vs. Other Cable Tray Materials
Steel Cable Trays vs. FRP Cable Trays
Steel cable trays are strong but prone to rust and corrosion over time, especially in high-moisture environments. FRP, on the other hand, offers superior resistance to corrosion without compromising strength. While steel trays may be more cost-effective initially, the maintenance costs associated with steel trays often outweigh those of FRP trays in the long run.
Aluminum Cable Trays vs. FRP Cable Trays
Aluminum trays are lighter than steel but still susceptible to corrosion under certain conditions. FRP, however, offers a better balance between weight and durability, making it a more versatile option in various industries. While aluminum may be suitable for some applications, FRP trays perform better in environments exposed to chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of FRP cable trays may be higher than other materials, their long-term cost-effectiveness is significant. The durability, low maintenance, and resistance to corrosion make FRP trays a more affordable option over time. In industries where downtime or maintenance costs are high, investing in FRP trays can result in substantial savings.
Here’s a comparison table showing the key differences between common cable tray materials:
Material | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Weight | Maintenance | Cost |
FRP | Excellent | High | Light | Low | Higher upfront |
Steel | Poor (rust prone) | Very High | Heavy | High | Lower upfront |
Aluminum | Moderate | Moderate | Light | Moderate | Moderate |
Installation of FRP Cable Trays
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Installing FRP cable trays involves several steps:
1. Planning: Determine the route for the trays and the required tray size based on the cables to be managed.
2. Preparation: Ensure that the installation area is clear, and safety measures are in place.
3. Mounting: Use brackets to securely attach the trays to walls, ceilings, or structural supports.
4. Cable Placement: Lay the cables within the trays, ensuring they are organized and safely secured.
5. Testing: Once the installation is complete, conduct tests to ensure the system is functioning as expected.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
● Improper Support: Inadequate support for the trays can lead to sagging or shifting, which can damage cables.
● Overcrowding: Avoid overloading the trays with too many cables. This can cause overheating and interfere with the safe operation of the system.
● Neglecting Airflow: In some installations, particularly with perforated trays, it’s crucial to maintain airflow to prevent cables from overheating.
Maintenance and Longevity of FRP Cable Trays
Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining FRP cable trays is relatively easy. Regular cleaning to remove dust and debris ensures proper airflow around the cables. Inspecting the trays for cracks or wear, especially after exposure to extreme conditions, is essential to ensure long-term durability.
Factors Affecting Longevity
Environmental factors such as exposure to high humidity, chemicals, or UV radiation can impact the lifespan of FRP trays. However, FRP is designed to withstand these elements better than most other materials. To extend the longevity of your trays, ensure they are installed in the right environment and regularly checked for any damage.
Troubleshooting FRP Cable Trays
● Cracking or Damage: If you notice any cracks or breaks in the tray, it may be due to mechanical stress or impact. Replace the damaged sections promptly.
● Overheating: Ensure that the trays are not overloaded and that adequate airflow is maintained to prevent overheating of cables.
Conclusion
FRP cable trays offer a robust, long-lasting, and cost-effective solution for managing cables in various industrial and commercial settings. Their resistance to corrosion, lightweight construction, and low maintenance requirements make them an ideal choice for challenging environments. By choosing FRP, businesses can reduce maintenance costs and increase the reliability of their cable management systems. Ongoing advancements in FRP materials will continue to enhance the performance and applications of FRP cable trays. As industries demand more sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions, FRP trays will play an even larger role in the future of electrical infrastructure. With continuous innovation, FRP cable trays are set to remain a key component of modern cable management systems.
Tip: When selecting FRP cable trays for your next project, always consider the environmental conditions and long-term cost savings. Choosing the right tray type and ensuring proper installation can significantly improve your system’s efficiency and lifespan. Consider working with trusted manufacturers like Avatar Composite Co., Ltd., a leader in FRP cable tray production.
FAQ
Q: What is an FRP cable tray?
A: An FRP cable tray is a type of cable management system made from fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP). It is used to support and organize electrical cables, offering superior corrosion resistance and strength while being lightweight and easy to install.
Q: How does an FRP cable tray differ from other cable trays?
A: FRP cable trays offer better corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel or aluminum trays. They are lighter, more durable in harsh environments, and require less maintenance, making them ideal for industries exposed to chemicals and moisture.
Q: Why should I choose an FRP cable tray for my project?
A: FRP cable trays are ideal for environments with high humidity, chemical exposure, or extreme weather. They offer long-term cost savings due to their low maintenance needs and resistance to corrosion, making them a smart investment for many industries.
Q: What are the main advantages of using FRP cable trays?
A: The main advantages of FRP cable trays include excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight design, high strength, and low maintenance costs. They are also fire-resistant and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for various industrial applications.















